How I built KinConnect to win 2000$ of Fireworks AI?
Here is my story of building a low-code low-cost RecSys for finding teammates for a hackathon!
I write about experimentation with synthetic data, scoping down a solution and getting an end to end RAG application out with multiple OSS LLMs, MongoDB Hybrid Search.
If this sound interesting, read on…
I started with: Is it possible to turn a hackathon into a melting pot of startup ideas and invaluable connections for future innovators and builders?
Imagine anyone—even your introvert geniuses—being able to thrive in a team of individuals sharing the same goal of wining a hackathon.
My team KinConnect wanted to get to the bottom of it at the MongoDB GenAI Hackathon[1] in Mountain View, CA.
My motivation: I had struggled to find great team members and always felt it was random. I believed there had to be a better way. We all answer the participation request survey with questions like, “What is the idea you want to hack on?”, “What are some projects you are proud of?” … There has to be a better way!
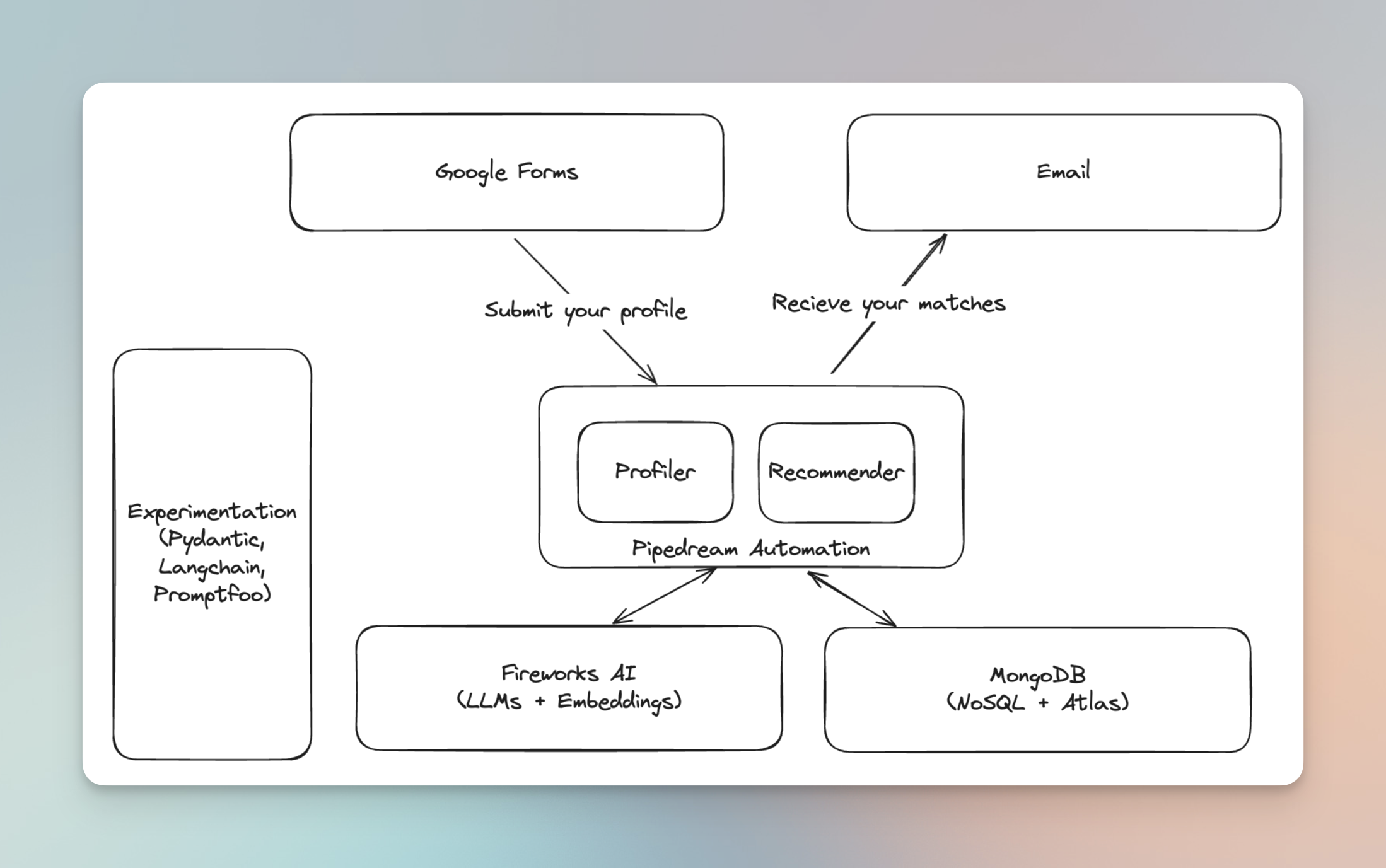
So my team KinConnect[2] embarked on a journey: Build a tool to help organizers and participants make better teams for the hackathons using real signal from the surveys.
While speaking with Gina, who is a community manager herself, we discussed the ingredients which make successful connections at these events. Gen AI alone wont be able to automate it all the way, so we wanted to build a tool for the organizer to manage community members and help in team formation.
This puzzle had two parts: rich participant profiles and a solid matching algorithm.
Because we only had a few hours to build and demo this, we brainstormed and divided the components into digestible chunks. We were going to do: Profile creation and verification, Profile matching and explanation, UI/UX, Data creation and testing.
Of course, given it’s a hackathon, we wanted to scope it down to what is possible in 4-5 hours.
User Flow:
- User creates a profile by filling a form. For the hackathon we used this google form.
- They get a confirmation email after their profile has been ingested into the database.
- They get an email with up to 5 matches.
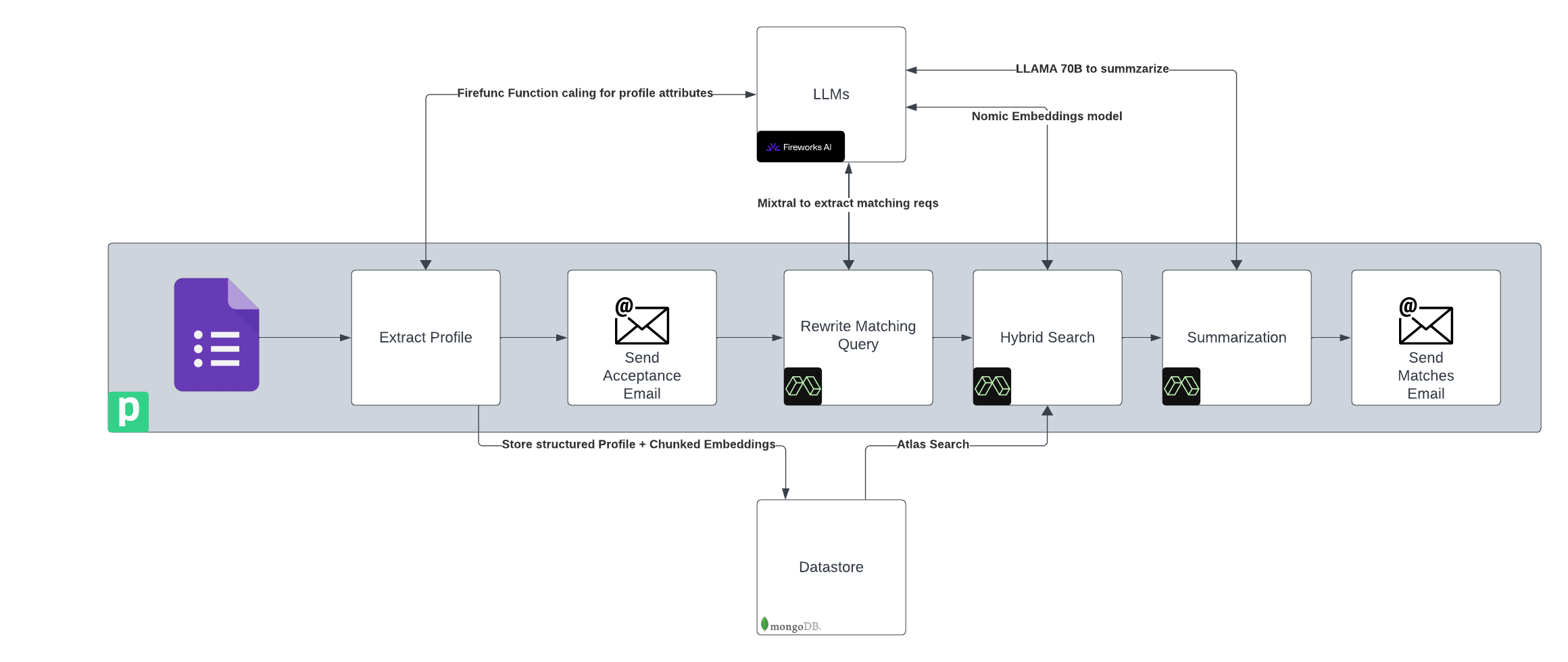
Our technical architecture:
UI:
In the theme of scoping things down, we decided not to build a custom UI and rather use Google Forms. This gives us the flexibility to easily change the questions and store the responses. They are even editable if people want to add more details or change their previous responses.
To show the matches, we chose email. Simply, get an email from the AI when matches have been found.
Backend:
We build two components in the backend. Profiler and recommender. The original two pieces of the puzzle, remember! We used pipedream for event driven integration of google forms and our backend. Its a no-code platform which allows you to build automated workflows with apps and custom code. We off-loaded complex compute to Modal Labs, hosting a FastAPI for doing the matching.
Fireworks AI:
We wanted to test how different models perform for our tasks. Fireworks gave us ability to use Llama3 and Mistral with function calling. They were sponsoring the event with credits which made it easier to start hitting the endpoints and experimenting.
Because Fireworks AI made all their models OpenAI compatible, it was easy to integrate with existing tools that don’t support fireworks out of the box.
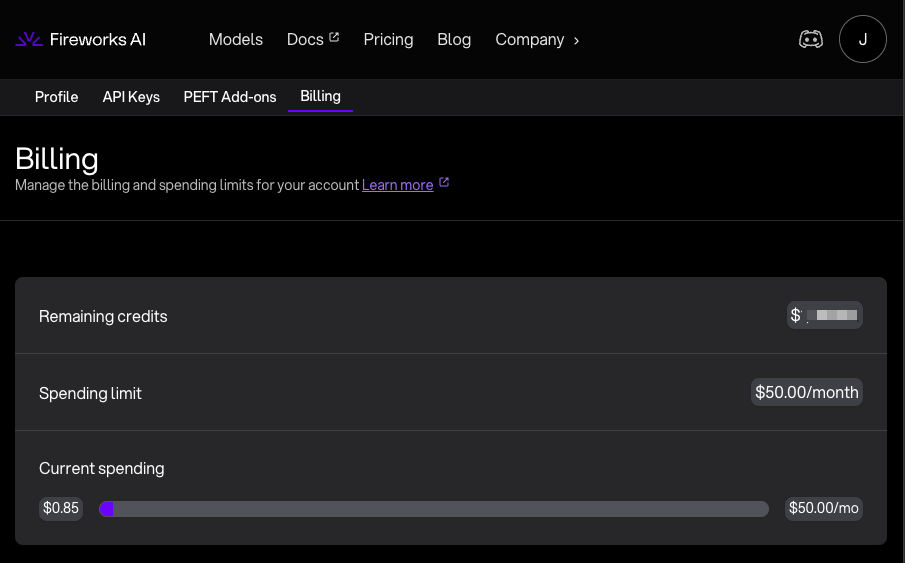
All of the development costed me << 1$ 🤯
MongoDB:
Another sponsor of the event is a popular mature database technology. Because each questionnaire can be different document store like mongodb suits the bill perfectly. We wanted to employ Hybrid search to in our matching algorithm. Hybrid = Vector Search + Text Search. MongoDB has a great tutorial on how to do Hybrid Search for RAG all inside the db.[3]
Many experts like @jobergum[4] from Vespa Engine talk about why Hybrid search is important for optimizing retrieval. Here is what he said recently:
In our reciprocal rank fusion, we found that keyword search has higher signal than semantic search so we weighted it higher.
Experimentation:
I have learned that the key to making a successful LLM app is experimenting and evaluating different prompts, llms and methods for a given task. So from the start I wanted to make sure we can iterate and evaluate the outputs from LLMs quickly. We used promptfoo for it. Some of our team members focused on creating fake but real looking profiles by filling a google form.
So how did it turn out?
You can try it out by filling this form. I would love feedback if you do 🙂. Please reach out at @nehiljain.
My highlights and lessons from the day of hacking:
Experiment with Promptfoo to get the prompts right
Using promptfoo we setup prompts with various fireworks AI models to test which works for our use case. We used LLMs for many tasks in our backend.
We generated synthetic profile data, created structured attributes from form submissions, rewrite user requests during our matching algo and generated summary explanation using a mixture of models.
Here is an example set of results: Parsing structured career history from the form submissions.

What we found with experimentation is that most of the smaller LLMs were not able to parse complex nested data structures but when we break down the task to smaller chunks they excelled at it.
Smaller models have trouble extracting complex nested structured outputs like these from the input text. Look at the ProfileModel class which composes an object with list of Career Entries and Project Entries.
class CareerEntry(BaseModel):
company: str
title: str
description: str
start_date: str
end_date: str
class ProjectEntry(BaseModel):
title: str
description: str
class ProfileModel(BaseModel):
name: str = Field(..., title="Name of the person")
honors: list[str] = Field(None, title="Honors, Awards and recognition they have recieved in life")
interests: list[str] = Field(..., title="Interests and current focus of theirs the work or the event")
skills: list[str] = Field(..., title="Skills they have")
career: List[CareerEntry] = Field(..., title="Career history of the person")
past_projects: List[ProjectEntry] = Field(..., title="Projects they have worked on")
elevator_pitch: str = Field(..., title="Elevator pitch for the person for the event")
But if I break it down to individual tasks for Career History, Portfolio and Profile Details like below, it works very well. Here is an example of how we extracted Portfolio.
class ProjectEntry(BaseModel):
title: str = Field(..., title="Title of the project")
description: str = Field(..., title="Description of the project")
class Portfolio(BaseModel):
projects: List[ProjectEntry] = Field(..., description="All the projects you have worked on")
All the code for experimentation can be found in the repository[5]
Launch Your Hackathon App quickly with Synthetic Data
Imagine building your app with a real looking dataset from the start. You can design a better UX, thoroughly test your matching algorithms, and write solid assertions. Synthetic data turns your vision into a robust reality from day one.
We used mixtral-8x22b-instruct for generating synthetic form submissions.
Our observation?
LLMs still struggle with diversity in synthetic data generation, but they offer a promising start. We had to hack together some pieces together to get it right.
Synthetic data generation at scale is a unsolved problem people are working on. This approach could be promising.
Use Pipedream/Zapier to reduce your code footprint
We wanted to integrate 4 components - Google Forms, Email, MongoDB, APIs together. Writing the boilerplate code and hosting it on some cloud server can be a rabbit hole that can take days. For hackathon, we were not worried about cost at scale, so we relied on low-code workflow automation tools.
This is what my backend looks like:
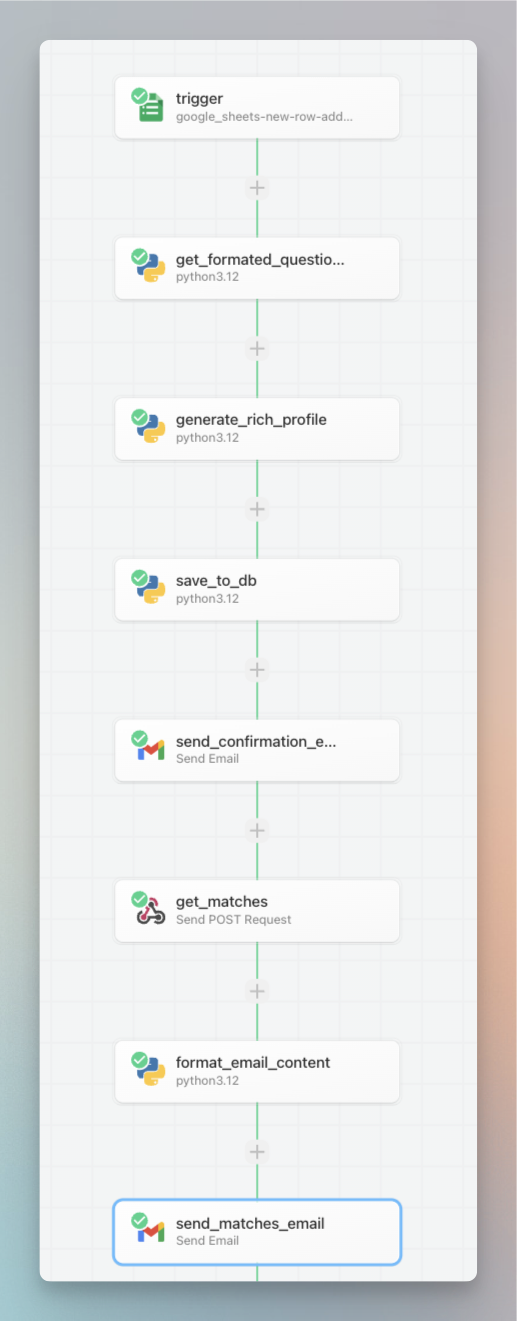
Other details:
- We used
llama-v3-70b-instructto rewrite queries into detailed, rich queries. Users often give brief descriptions, so detailed queries improve accuracy. - We used excellent docs on MongoDB https://www.mongodb.com/docs/atlas/atlas-vector-search/ai-integrations/langchain/ to quickly integrate with MongoDB as our data store.
The repository[5:1] has all the prompts and code.
My takeaways for winning:
- Doing one thing well can help you win a Hackathon.
- If you don't have a UI use a great deck to present the idea and solution clearly
- Function calling is a great way to build reliable applications on top of LLM. Fireworks gives you much cheaper models to work with.
- Fireworks allows you to interact with their models on OpenAI chat api spec. I love to see the industry converge on 1 standard so that developers can standardize the tooling on top of it.
Next Steps:
- Add data enrichment modules by scraping LinkedIn and Github
- Build a robust and flexible matching algorithm
- Trial this as a bot in discord and slack for next hackathons we attend
In the end, we learned a lot. There was awesome camaraderie in our team, which helped us push all day till the end. The food was awesome. Thank you Karissa and Team from MongoDB to host us. Winning was the cherry on top of this experience and will help us bring our idea to the next level by taking it to a production ready scale with Fireworks AI LLM credits. This is a great read for my future self. How to optimize LLM inference for my workload
I am bullish that the features and integrations built into MongoDB make it a great one-size-fits-all database for app developers. I know 'Postgres is all you need' is another sentiment floating around in the AI engineering community, but I think MongoDB is well-poised to be a great db for the Gen AI stack.
I you are a hackathon organizer or participant who would like to try it, please reach out @nehiljain
MongoDB GenAI Hackathon with AWS, sponsored by Fireworks AI & Unstructured.io ↩︎
My team KinConnect, named because we connect you to your 'Kins' ↩︎
Mongo DB has powerful syntax to do data transformation and searching in the db. A tutorial from them for how to do hybrid search is a great place to learn it. ↩︎
The common advice from experts in RAG is used BM25 or atleast test it out. Jo Tweeted this recently as well. ↩︎
Code Repo is [here] https://github.com/nehiljain/kinconnect/ ↩︎ ↩︎